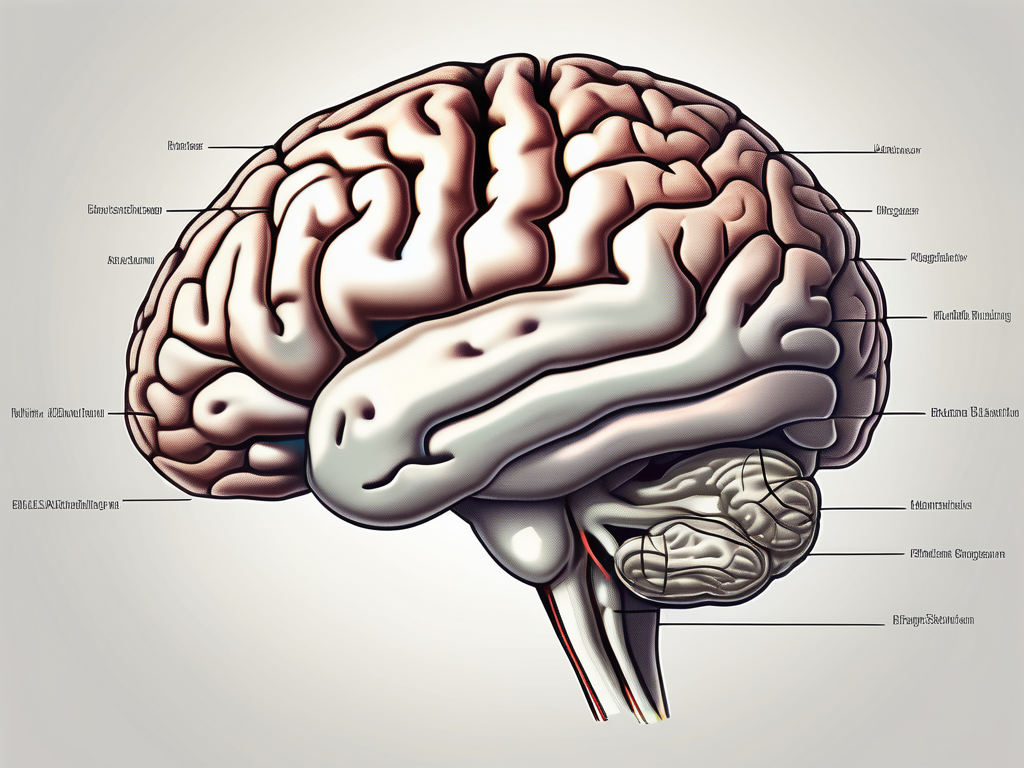
The trochlear nerve, also known as cranial nerve IV, plays a crucial role in the functioning of our visual system. Understanding the origin, function, and disorders related to this nerve can provide valuable insights into the intricate workings of our brain and visual system. In this article, we will explore the trochlear nerve in detail, discussing its definition, anatomy, origin, role in vision, disorders, and recent research advancements. Please note that while we aim to provide informative content, this article does not constitute medical advice, and it is always advisable to consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Understanding the Trochlear Nerve
The trochlear nerve is the fourth cranial nerve and is responsible for controlling the superior oblique muscle of the eye. This muscle allows for specific eye movements, such as downward and inward rotation. To fully comprehend the significance of this nerve, let’s delve into its definition and function as well as its intricate anatomy.
Definition and Function of the Trochlear Nerve
The trochlear nerve originates in the midbrain and is primarily responsible for innervating the superior oblique muscle of the eye. This muscle aids in downward and inward eye movement, allowing us to focus on objects within our visual field. Without the proper functioning of the trochlear nerve, these eye movements can become impaired, leading to various visual disturbances.
Understanding the trochlear nerve’s function is crucial in appreciating its role in our visual system. When we look down or inward, the superior oblique muscle contracts, causing the eye to rotate in a specific direction. This movement allows us to track objects as they move within our field of vision, ensuring clear and accurate visual perception.
Moreover, the trochlear nerve’s precise control over the superior oblique muscle enables us to perform complex eye movements, such as reading, writing, and following moving objects. These actions rely on the coordinated functioning of multiple cranial nerves and muscles, with the trochlear nerve playing a vital role in ensuring smooth and accurate eye movements.
Anatomy of the Trochlear Nerve
The trochlear nerve emerges from the dorsal surface of the brainstem, specifically from the trochlear nucleus located in the midbrain. Unlike other cranial nerves, the trochlear nerve decussates (crosses over) within the brainstem, resulting in a unique pathway. After crossing over, the nerve exits the brainstem dorsally, forming a gentle curve as it travels towards the superior oblique muscle of the eye.
As the trochlear nerve travels towards its destination, it navigates through a complex network of structures within the brainstem. These structures include the midbrain tegmentum, the red nucleus, and the substantia nigra. The intricate interplay between these regions and the trochlear nerve ensures precise control over the superior oblique muscle, allowing for accurate eye movements.
Furthermore, the trochlear nerve’s pathway within the brainstem highlights the intricate nature of our nervous system. The decussation of the nerve fibers ensures that the appropriate signals from the brain reach the correct eye muscle, facilitating coordinated and synchronized movements.
It is essential to grasp the pathway and location of the trochlear nerve within the brain to comprehend its origin and its subsequent role in visual function. By understanding the intricate anatomy of this nerve, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and precision of our visual system.
Origin of the Trochlear Nerve in the Brain
The trochlear nerve’s exact location within the brain and its connection to the midbrain are critical in understanding how this nerve operates and influences our visual abilities.
Location and Pathway of the Trochlear Nerve
The trochlear nerve emerges from the dorsal aspect of the brainstem, specifically from the trochlear nucleus. This nucleus, located in the midbrain, plays a crucial role in the coordination of eye movements. From the trochlear nucleus, the nerve fibers of the trochlear nerve travel in a distinctive loop, crossing over within the brainstem before exiting towards the superior oblique muscle.
The superior oblique muscle is responsible for rotating the eye downward and outward. The trochlear nerve’s intricate pathway allows for precise control of this muscle, ensuring accurate eye movement and coordination. This precise control is essential for activities such as reading, tracking moving objects, and maintaining proper alignment of the eyes.
Connection to the Midbrain
Being connected to the midbrain, the trochlear nerve is closely associated with other essential structures involved in visual processing. The midbrain serves as a relay station, transmitting visual information from the eyes to higher brain regions responsible for perception and interpretation.
Within the midbrain, the trochlear nerve interacts with the oculomotor nerve, which controls the movement of other eye muscles. This interaction allows for coordinated eye movement, ensuring both eyes work together harmoniously to capture and process visual information accurately.
In addition to the oculomotor nerve, the trochlear nerve also interacts with the optic nerve, responsible for transmitting visual signals from the retina to the brain. This intricate network of nerve connections within the midbrain ensures that visual information is efficiently processed and integrated, leading to a clear and coherent visual experience.
Overall, the trochlear nerve’s origin in the brain and its connection to the midbrain highlight its importance in visual function. Its precise pathway and interactions with other crucial structures ensure that our eyes can move accurately and work together seamlessly, allowing us to perceive the world around us with clarity and depth.
Role of the Trochlear Nerve in Vision
The trochlear nerve’s influence extends beyond its anatomical connections. Understanding the nerve’s role in vision provides insights into how it interacts with other cranial nerves and contributes to our visual perception.
The trochlear nerve, also known as the fourth cranial nerve or CN IV, is a motor nerve that innervates the superior oblique muscle of the eye. This muscle is responsible for rotating the eye downward and outward, allowing us to look down and away from the midline. However, the trochlear nerve’s involvement in vision goes beyond its role in eye movement control.
Control of Eye Movement
The trochlear nerve, in conjunction with various other cranial nerves, plays a vital role in coordinating eye movements. These movements facilitate smooth tracking of objects, depth perception, and overall visual stability. Dysfunction of the trochlear nerve can result in difficulties in tracking moving objects or a lack of coordination between the two eyes, leading to visual disturbances.
When we look at an object, our eyes need to work together to focus on it and follow its movement. This coordination is achieved through the interaction of multiple cranial nerves, including the trochlear nerve. The trochlear nerve helps to control the superior oblique muscle, which aids in downward and outward eye movement. This movement is essential for tracking objects as they move across our visual field.
Imagine watching a bird flying across the sky. As it moves, our eyes need to smoothly track its path to maintain a clear and stable image. The trochlear nerve, along with other cranial nerves, ensures that our eyes work together harmoniously to achieve this tracking ability. Without the trochlear nerve’s contribution, our eyes might struggle to follow the bird’s flight path, resulting in a jerky and fragmented visual experience.
Interaction with Other Cranial Nerves
The trochlear nerve, like other cranial nerves, works in tandem with other neural pathways within the brain to ensure coordinated eye movements and visual processing. Its integration with the visual pathway and the intricate interplay between various cranial nerves contribute to our ability to perceive and interpret visual information effectively.
Visual processing is a complex task that involves multiple regions of the brain working together. The trochlear nerve plays a crucial role in this process by connecting with other cranial nerves, such as the oculomotor nerve (CN III) and the optic nerve (CN II). These connections allow for the transmission of information between different parts of the visual system, enabling us to make sense of the world around us.
For example, when we see an object, the optic nerve carries visual information from the retina to the brain. The trochlear nerve then collaborates with the oculomotor nerve to coordinate the appropriate eye movements needed to focus on the object. This integration of neural pathways ensures that our eyes move in sync with our visual attention, allowing us to explore our environment and gather visual information efficiently.
In summary, the trochlear nerve’s role in vision extends beyond its anatomical connections. It is involved in coordinating eye movements, facilitating smooth tracking of objects, and contributing to overall visual stability. Additionally, its interaction with other cranial nerves within the visual pathway ensures effective visual processing and interpretation. Understanding the intricate workings of the trochlear nerve enhances our knowledge of the complexities of vision and the remarkable mechanisms that enable us to see the world around us.
Disorders Related to the Trochlear Nerve
When the trochlear nerve’s functionality is compromised, several disorders can arise, affecting visual abilities and overall visual comfort. It is important to be aware of the potential symptoms, the diagnosis process, and available treatment options for these disorders.
The trochlear nerve, also known as the fourth cranial nerve, plays a crucial role in eye movement. It innervates the superior oblique muscle, which is responsible for rotating the eye downward and inward. Any damage or dysfunction in this nerve can lead to various visual impairments and discomfort.
Symptoms of trochlear nerve damage can vary depending on the extent and location of the injury. One common symptom is double vision, also known as diplopia. This occurs because the affected eye is unable to align properly with the other eye, causing overlapping images. Individuals with trochlear nerve damage may also experience difficulty with downward and inward eye movements, making it challenging to look down or focus on objects close to them.
Another symptom that may arise from trochlear nerve damage is difficulty with reading or focusing on close-up objects. This can significantly impact daily activities such as reading, writing, or working on a computer. Individuals may find it hard to maintain clear and stable vision when looking at objects up close, leading to eye strain and fatigue.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. A comprehensive evaluation conducted by an eye specialist or neurologist is typically necessary to determine the underlying cause of the trochlear nerve disorder.
Diagnosing trochlear nerve disorders involves a thorough examination of the eyes and a detailed medical history assessment. The healthcare professional will evaluate eye movements, check for any muscle weakness or imbalance, and perform additional tests if needed. These tests may include imaging studies, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), to identify any structural abnormalities or lesions affecting the trochlear nerve.
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, the treatment approach for trochlear nerve disorders depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to manage symptoms or address any underlying inflammation or infection. Vision therapy, which involves exercises and techniques to improve eye coordination and control, may also be recommended to enhance visual function.
In more severe cases or when conservative treatments are ineffective, surgical interventions may be considered. Surgical options for trochlear nerve disorders aim to correct any anatomical abnormalities or repair damaged nerve pathways. These procedures are typically performed by specialized ophthalmic or neuro-ophthalmic surgeons and require careful evaluation and planning.
Seeking professional medical advice is essential for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. Early intervention and management of trochlear nerve disorders can significantly improve visual function and overall quality of life.
Recent Research on the Trochlear Nerve
Ongoing research in the field of neurology continues to shed light on the intricacies of the trochlear nerve and its impact on visual function. Advancements in understanding this nerve have significant implications for future treatment and therapeutic strategies.
The trochlear nerve, also known as the fourth cranial nerve, is responsible for controlling the superior oblique muscle of the eye. This muscle plays a crucial role in eye movement, allowing us to look down and inward. Dysfunction of the trochlear nerve can lead to a range of visual impairments, including double vision, difficulty with downward gaze, and problems with depth perception.
Advances in Neurological Understanding
Recent studies have provided new insights into the mechanisms underlying trochlear nerve disorders, exploring potential causes and interventions. These advancements deepen our understanding of the trochlear nerve’s complexities and open doors for targeted treatment options.
One recent study published in the Journal of Neurology examined the role of neuroinflammation in trochlear nerve dysfunction. The researchers found that inflammation in the nerve can disrupt the transmission of signals, leading to visual disturbances. This discovery highlights the importance of addressing inflammation as a potential therapeutic target for trochlear nerve disorders.
Another study conducted at a leading research institution investigated the genetic factors contributing to trochlear nerve abnormalities. By analyzing the DNA of individuals with trochlear nerve disorders, the researchers identified specific gene mutations associated with the condition. This breakthrough provides a foundation for future genetic therapies aimed at correcting these mutations and restoring normal trochlear nerve function.
Future Implications for Treatment and Therapy
The growing body of research on the trochlear nerve holds promise for future advancements in treatment and therapy for individuals with trochlear nerve disorders. From innovative surgical techniques to novel therapeutic interventions, this research paves the way for potential breakthroughs in optimizing visual function and improving the quality of life for those affected.
One area of ongoing research focuses on the development of neurostimulation techniques to enhance trochlear nerve function. By using electrical stimulation to activate the nerve, researchers aim to improve eye movement coordination and alleviate symptoms associated with trochlear nerve disorders. Preliminary studies have shown promising results, with patients experiencing improved visual acuity and reduced double vision.
Additionally, advancements in regenerative medicine offer hope for restoring damaged trochlear nerves. Scientists are exploring the use of stem cells to repair and regenerate damaged nerve tissue, potentially reversing the effects of trochlear nerve disorders. This cutting-edge approach holds great potential for individuals who have experienced trauma or degeneration of the trochlear nerve.
In conclusion, the trochlear nerve plays a crucial role in our visual system, controlling eye movement and contributing to our overall visual abilities. Understanding the origin, function, disorders, and recent research advancements related to this nerve provides valuable insights into the intricate workings of our brain and visual system. Remember that while this article provides informative content, it is not a substitute for professional medical advice. If you experience any symptoms or concerns related to the trochlear nerve, consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance tailored to your specific needs.