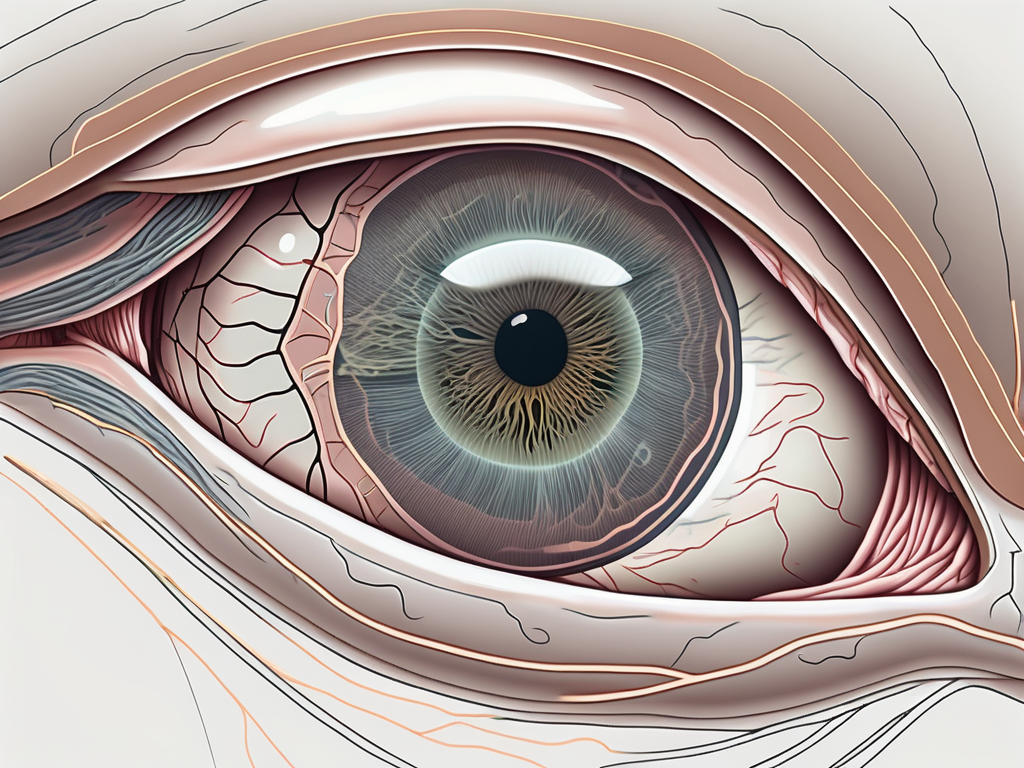
The intricate structure of the human eye is a marvel of nature. It is a well-orchestrated symphony of various components working together to provide us with the sense of vision. Within this delicate system, the role of intrinsic eye muscles cannot be underestimated. These muscles play a crucial part in controlling the movement and alignment of the eye.
Understanding the Structure of the Eye
To truly appreciate the intricacies of the eye’s intrinsic eye muscles, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of the eye’s structure. The eye, a remarkable organ, is composed of numerous interconnected parts, each with its own specific function and purpose.
At the forefront of the eye is the cornea, a transparent, dome-shaped structure that acts as a protective barrier, shielding the delicate inner components from harm. It not only allows light to enter the eye but also plays a crucial role in focusing the incoming light onto the retina.
Located behind the cornea is the iris, the colorful part of the eye that gives each individual their unique eye color. The iris acts as a natural diaphragm, controlling the amount of light that enters the eye by adjusting the size of the pupil. This remarkable mechanism allows us to adapt to varying light conditions, ensuring optimal vision in different environments.
Deep within the eye lies the lens, a clear, flexible structure responsible for fine-tuning the focus of incoming light onto the retina. Through a process called accommodation, the lens adjusts its shape to allow us to see objects clearly at different distances. This remarkable ability enables us to shift our focus effortlessly, whether we are admiring a distant mountain range or reading a book up close.
Finally, at the back of the eye, we find the retina, a thin layer of tissue that contains millions of specialized cells called photoreceptors. These photoreceptors, known as rods and cones, convert light into electrical signals, which are then transmitted to the brain via the optic nerve. The brain interprets these signals, allowing us to perceive the world around us in vivid detail.
The Role of Intrinsic Eye Muscles
While the external components of the eye are essential for its overall function, the intrinsic eye muscles, nestled within the eye itself, play a pivotal role in fine-tuning our visual experience. These remarkable muscles, although minuscule in size, possess an unparalleled precision that allows for delicate and precise movements.
Unlike the extrinsic eye muscles, which are responsible for moving the eye in different directions, the intrinsic eye muscles work in harmony with their external counterparts to ensure optimal vision. These intrinsic muscles, although less known, are equally vital in maintaining the eye’s overall functionality.
One of the key intrinsic eye muscles is the ciliary muscle, which surrounds the lens. This muscle plays a crucial role in the process of accommodation, allowing the lens to change its shape and adjust its focal length. Through the contraction and relaxation of the ciliary muscle, the lens can effortlessly adapt to different distances, ensuring that objects at varying distances remain in clear focus.
Another important intrinsic eye muscle is the sphincter pupillae muscle, located within the iris. This muscle is responsible for constricting the pupil, reducing its size in bright light conditions. By narrowing the pupil, the sphincter pupillae muscle limits the amount of light entering the eye, preventing overwhelming brightness and ensuring optimal visual clarity.
The Function of the Trochlear Nerve
Among the intricate network of nerves that control the eye’s movements, the trochlear nerve, also known as cranial nerve IV, stands out as a remarkable component. This nerve, originating from the brainstem, is the longest of all cranial nerves, extending its reach to the superior oblique muscle.
The superior oblique muscle, one of the six extrinsic eye muscles, plays a crucial role in specific eye movements, particularly those involving downward and inward rotations. The trochlear nerve, with its unique positioning, sends signals to the superior oblique muscle, enabling it to perform its intricate movements with precision.
Through the coordinated efforts of the trochlear nerve and the superior oblique muscle, our eyes can effortlessly navigate the world around us. Whether we are reading a book, tracking a moving object, or simply gazing at the beauty of nature, these intricate mechanisms work together to ensure our visual experience is seamless and precise.
The Trochlear Nerve and Eye Movement
Now that we understand the role of the trochlear nerve, let’s delve deeper into its connection with eye movement.
The trochlear nerve, also known as the fourth cranial nerve, is a small but mighty nerve that plays a crucial role in controlling eye movement. It is the smallest cranial nerve in terms of the number of axons it contains, but its impact on vision cannot be underestimated.
The Connection between the Trochlear Nerve and Superior Oblique Muscle
The trochlear nerve is responsible for innervating the superior oblique muscle, one of the six extrinsic muscles surrounding the eye. This muscle is unique in its orientation and function, as it is the only muscle that originates from the back of the eye socket and inserts on the top of the eye.
When the trochlear nerve sends signals to the superior oblique muscle, it causes the muscle to contract and perform specific movements. The superior oblique muscle plays a crucial role in depressing the eye (looking downward) and rotating it inward toward the nose. This movement is essential for situations such as reading or viewing objects from a close distance.
Imagine trying to read a book without the ability to rotate your eyes inward. It would be incredibly challenging to focus on the words and follow the lines. The trochlear nerve, working in harmony with the superior oblique muscle, allows us to effortlessly perform these tasks.
How the Trochlear Nerve Affects Vision
Damage or dysfunction of the trochlear nerve can have a significant impact on vision and overall eye movement. When the trochlear nerve is compromised, it can lead to a condition known as trochlear nerve palsy.
Individuals with trochlear nerve disorders may experience symptoms such as double vision, difficulty focusing, or an abnormal head tilt to compensate for impaired eye movement. These symptoms can greatly affect daily activities and quality of life.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional if any such symptoms develop. They can perform a thorough examination and determine the underlying cause of the trochlear nerve dysfunction. Treatment options may include medication, vision therapy, or in severe cases, surgery.
The trochlear nerve and its connection to eye movement are fascinating examples of the intricate workings of the human body. Understanding the role of this nerve helps us appreciate the complexity and precision required for even the simplest of tasks, such as looking at an object. So the next time you effortlessly read a book or admire a beautiful view, remember to thank your trochlear nerve for its vital contribution to your vision.
Disorders Related to the Trochlear Nerve
While the trochlear nerve is a vital component of our visual system, it is susceptible to various disorders that can disrupt its proper functioning.
The trochlear nerve, also known as the fourth cranial nerve, is responsible for controlling the movement of the superior oblique muscle in the eye. This muscle plays a crucial role in our ability to move our eyes in different directions, allowing us to focus on objects at varying distances. However, when the trochlear nerve is damaged or affected by a disorder, it can lead to a range of symptoms and visual disturbances.
Symptoms of Trochlear Nerve Damage
The symptoms of trochlear nerve damage can vary depending on the extent and location of the injury. However, common signs include double vision (especially when looking downward or inward), difficulty reading or focusing on nearby objects, and eye misalignment. These symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, making simple tasks such as reading, driving, or even walking challenging and frustrating.
When the trochlear nerve is damaged, the communication between the brain and the superior oblique muscle is disrupted. As a result, the affected eye may not move properly, leading to misalignment and double vision. The brain tries to compensate for this misalignment by suppressing or ignoring the input from the affected eye, which can further contribute to visual disturbances.
Treatment and Management of Trochlear Nerve Disorders
Due to the complexity of the eye and its associated nerves, the treatment and management of trochlear nerve disorders require a specialized approach. It is crucial to seek medical attention if any symptoms of trochlear nerve damage are present, as early intervention can lead to better outcomes.
When diagnosing trochlear nerve disorders, ophthalmologists and neurologists may perform a comprehensive eye examination, including visual acuity tests, eye movement evaluations, and imaging studies. These assessments help determine the extent of nerve damage and guide the development of an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment options for trochlear nerve disorders may include medication, vision therapy, or, in more severe cases, surgery. Medications such as muscle relaxants or pain relievers can help alleviate symptoms and improve eye movement. Vision therapy, which involves exercises and techniques to strengthen eye muscles and improve coordination, can also be beneficial in managing trochlear nerve disorders.
In cases where conservative treatments are ineffective or the nerve damage is severe, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical procedures can involve repairing the damaged nerve or adjusting the position of the affected eye muscles to improve alignment and reduce double vision. These surgeries are typically performed by ophthalmologists who specialize in neuro-ophthalmology.
It is important to note that the specific treatment approach for trochlear nerve disorders may vary depending on individual circumstances. Therefore, it is essential to consult with an ophthalmologist or a neurologist for proper evaluation and guidance on the most appropriate course of action.
The Importance of Eye Muscle and Nerve Health
Preserving the health of our eye muscles and nerves is paramount for maintaining optimal vision and overall eye function.
Our eyes are remarkable organs that rely on a complex network of muscles and nerves to function properly. The eye muscles work together to control the movement of our eyes, allowing us to focus on objects and track moving targets. The nerves, on the other hand, transmit signals from the eyes to the brain, enabling us to process visual information and make sense of the world around us.
Maintaining Healthy Eye Muscles and Nerves
While some eye muscle and nerve disorders may be unavoidable, there are steps we can take to promote overall eye health. Regular eye examinations, especially as we age, can help identify any potential issues early on. These examinations typically involve a series of tests to assess the strength and coordination of the eye muscles, as well as the health of the optic nerves.
In addition to regular check-ups, practicing good eye hygiene is crucial for maintaining healthy eye muscles and nerves. This includes avoiding excessive screen time, as prolonged exposure to digital devices can strain the eye muscles and lead to discomfort and fatigue. Taking regular breaks and practicing the 20-20-20 rule, which involves looking at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds every 20 minutes, can help alleviate eye strain and reduce the risk of developing muscle imbalances.
The Impact of Overall Health on Eye Function
It is important to recognize that eye health is closely interconnected with our overall well-being. Conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and certain neurological disorders can have a profound impact on the health of our eyes and their associated nerves. For example, uncontrolled diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to a condition called diabetic retinopathy, which can cause vision loss if left untreated.
Therefore, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial for preserving the health of our eyes. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can provide the necessary nutrients to support eye health. Regular exercise, such as walking or swimming, can improve blood circulation and promote overall well-being, which in turn benefits the eyes. Additionally, managing chronic conditions through medication, lifestyle modifications, and regular medical check-ups can help minimize the risk of complications that can affect the eyes.
Furthermore, protecting our eyes from environmental factors is essential for maintaining their health. Wearing sunglasses with UV protection can shield the eyes from harmful ultraviolet rays, which can contribute to the development of cataracts and other eye conditions. Using safety goggles or protective eyewear when engaging in activities that pose a risk of eye injury, such as playing sports or working with power tools, is also crucial.
In conclusion, the health of our eye muscles and nerves is vital for maintaining optimal vision and overall eye function. By prioritizing regular eye examinations, practicing good eye hygiene, and taking care of our overall health, we can contribute to the longevity and well-being of our eyes. Let us cherish the gift of sight and make conscious efforts to preserve the intricate systems within our eyes.